사이토카인의 명명법
사이토카인의 명명법
,
사이토카인은 구조적으로 비슷한 군끼리 그룹화 되어진다.
그리고 접두어와 접미어로 이름이 만들어진다.
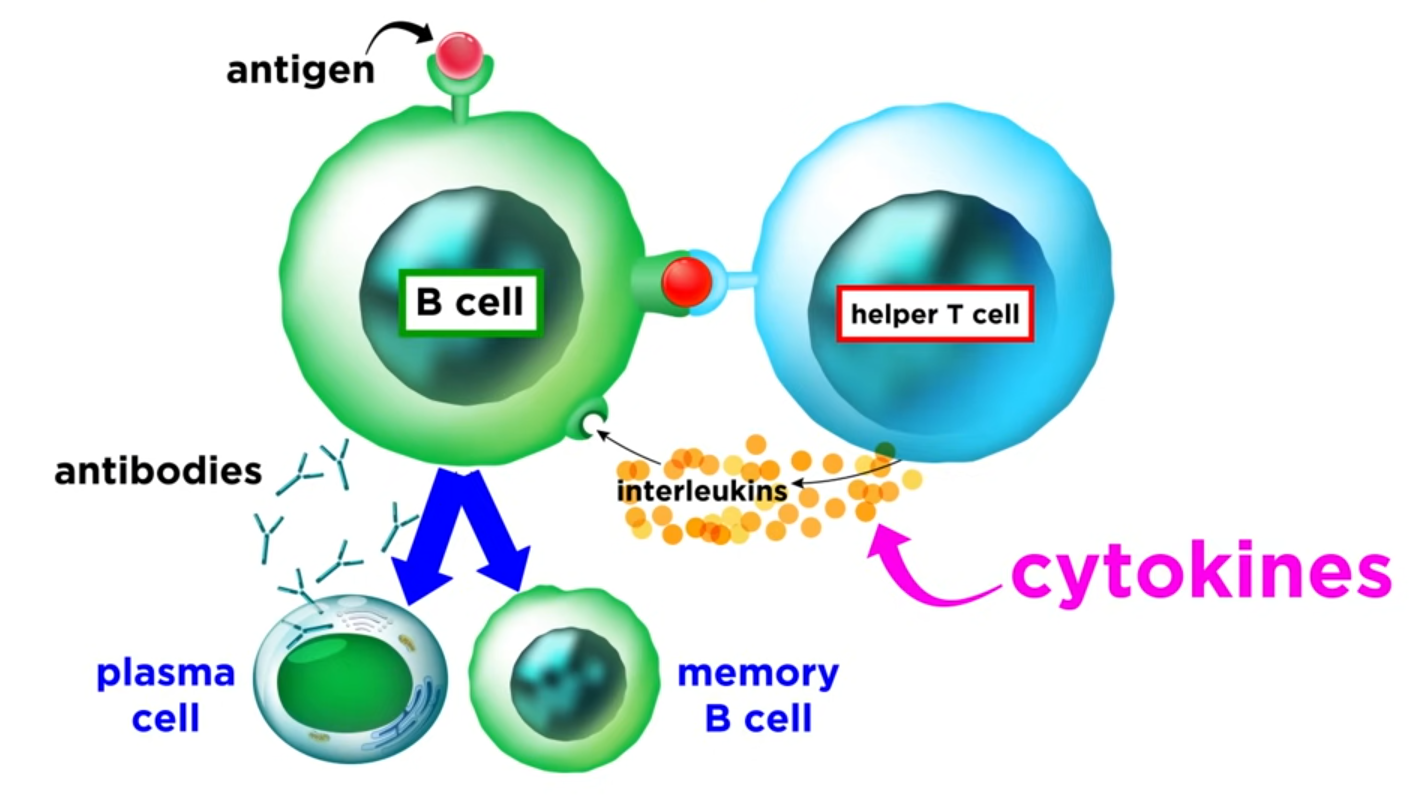
- -interleukins (IL-): 인터루킨, 백혈구(Leukocyte)에서 생성되고 백혈구 사이의 소통을 담당한다. 사이토카인의 가장 큰 군이다
- -interferons (IFN-): 인터페론, 항바이러스(antiviral) 감염에 관여
- -tumor necrosis factors (TNF-): 종양괴사인자
- -colony stimulating factors (-CSF): 조혈성장인자 또는 집락자극인자, 혈액세포의 성장에 도움
그 외
- Lymphokines: 림프구(Lymphocytes)에 의해 생성
- Monokines: 단핵구(Monocytes)에 의해 생성
- Chemokines: 화학주성(*chemotactic)의 활동을 갖는 사이토카인
*화학주성(chemotactic): 물질을 향해 이동하는 성질. 이웃 세포가 신호를 기반으로 자신을 향해 이동하거나 세포의 이러한 이동을 유발할 수 있는 화학적 요인을 의미.
*사이토카인의 명명법을 배웠으니 이제 줄임말로 사용하겠다!
대표적인 인터루킨 3가지
,
IL-1: 주요 면역 첫 번째 단계에서 사용되어짐
- 대식세포(Macrophages), 섬유아세포(Fibroblasts), 내피세포(Endothelial cells), 소수의 상피세포(Few epithelial cells)
- 내피에 부착된 분자의 발현을 자극
- 호중구(neutrophils) 및 대식세포(macrophages)의 이동
- 다른 사이토카인의 분비(secretion)
- 발열감
ㅇ
IL-6: 체액성 면역(humoral)
- 대식세포(Macrophages), 섬유아세포(Fibroblasts), 내피세포(Endothelial cells), 소수의 상피세포(Few epithelial cells)
- 면역 시스템 반응단계
1. 간에서 급성 반응물질 생산
2. B세포가 항체 생산세포(혈장세포(plasma cells))로 분화하도록 유도
IL17: 세포성 면역
- T림프구(T lymphocytes)
- 호중구(neutrophils)과 단핵구(monocytes)를 부름
- LI-6, G-SCF, GM-CSF, IL-β, TNF-α, chemokines과 같은 다른 사이토카인 분비
사이토카인과 케모카인이 구조적 유사성에 의해 그룹화 되어지고 발견의 순서에 따라 조직화 되어졌기 때문에, 다음 포스팅에서 비슷한 기능을 기반으로 각각에 대해 설명해보고자 한다.
사이토카인과 케모카인의 유형
,
| Cytokines / Chemokines | |
| *pro-inflammatory cytokines (PIC) |
IFN-γ(Interferon gamma) TNF-α(Tumor necrosis factor A) IL-12p40, IL-12p70 IL-1β, IL-1α, IL-17A, IL-6, IL-8 |
| *anti-inflammantory | IL-10, IL-13 |
| Chemokines | IFN-γ inducible protein (IP-10/CXCL-10) monocyte chemotactic protein 3 (MCP-3/CCL7) monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1/CCL2) monocyte inflammatory protein 1β (MIP-1β/CCL4) Fractalkine (FKN/CX3CL1) |
| Growth factor | GM-CSF(Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor), VEGF(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor), IL-2, IL-5 |
*pro-inflammatory cytokines(PIC): 감염이 일어났을 경우 항상 대기 중인 애들. 예를들어 감염이 일어났을 경우 빨갛게 부풀어(swelling reness) 오르는 경우가 있다. 즉, 우리 몸의 면역시스템이 실제로 감염과 싸우고 있다는 것을 의미한다.
*anti-inflammatory cytokines: 염증반응을 일으키지 않거나 염증 관련한 증상들을 줄여준다. 왜냐하면 염증반응은 우리 몸이 감염되는 동안 불편함과 다른 문제들을 일으킬 수 있기 때문이다.
- Cytokine Nomenclature
Cytokine are grouped into structurally similar families, and are named with a prefix(접두어) or suffix(접미어)
- -interleukins (LI-): One of the largest familes of cytokines. The name refers to communication between leukocytes or white blood cells
- -interferons (IFN-)
- -tumor necrosis factors (TNF-)
- -colony stimulating factors (-CSF)
- Interleukins: Produced by one leukocyte ad act on other leukocyte
- Lymphokines: Produced by Lymphocytes
- Monokines: Produced by Monocytes
- Chemokines: Cytokines which are having *chemotactic activities*chemotactic = chemotaxis that means a chemical factor which can cause the neighboring cells to move towards itself or this journey of the cells based on the signaling is known as chemotaxis
- Interferons: Involved in antiviral responses
- Colony stimulating factors: Supports the growth of blood cells
Because Cytokine and chemokine names are often grouped by struatural similarity and organized in order of discovery, we are going to introduce them based on similar function.
Interleukin-1: mostly used during the first of primary stages of immunity
- Macrophages, Fibroblasts, Endothelial cells, Few epithelial cells
- Stimulates expression of endothelial adhesion molecules.
- Emigration of neutrophils and macrophages
- Secretion of other cytokines
- Fever
Interleukin-6: humoral mediated immunity
- Macrophages, Fibroblasts endothelial cells, Few epithelial cells
Systemic Response:
- Production of Acute Phase Reactants from liver
- Particularly important in inducing B-cells to differentiate into antibody producing cells (plasma cells)
Interleukin-17: cell madiated immunity
- T lymphocytes
- Recruitment of neutrophils and monocytes
- Secretion of other cytokines like LI-6, G-SCF, GM-CSF, IL-β, TNF-α, chemokines.
- Types of Immune response named for the type of helper T cell involved
Let's just focus on the groups of cytokines that tend to function together, as well as the major outcomes of these signaling profiles.
- Types of cytokines and chemokines
| Cytokines / Chemokines | |
| *pro-inflammatory cytokines (PIC) |
IFN-γ(Interferon gamma) TNF-α(Tumor necrosis factor A) IL-12p40, IL-12p70 IL-1β, IL-1α, IL-17A, IL-6, IL-8 |
| *anti-inflammantory | IL-10, IL-13 |
| Chemokines | IFN-γ inducible protein (IP-10/CXCL-10) monocyte chemotactic protein 3 (MCP-3/CCL7) monocyte chemotactic protein 1 (MCP-1/CCL2) monocyte inflammatory protein 1β (MIP-1β/CCL4) Fractalkine (FKN/CX3CL1) |
| Growth factor | GM-CSF(Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor), VEGF(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor), IL-2, IL-5 |
pro-inflammatory cytokines(PIC) which are already present and active even before inflammantion in our body.
anti-inflammatory cytokines which will not cause any inflammation and reduce the symptoms associated with the inflammation. Because inflammation may cause many other discomforts and problems in our body during infection.